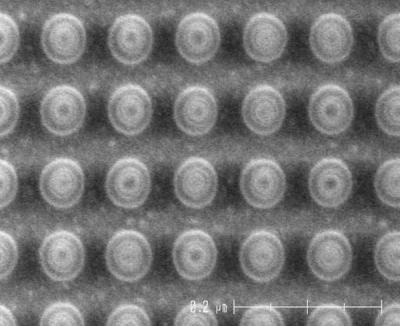
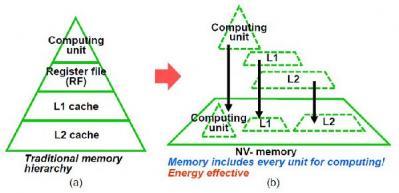
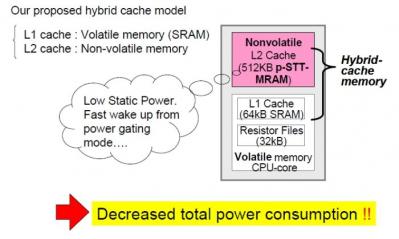
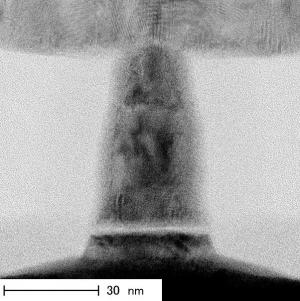
Toshiba developed new STT-MRAM technology that can be used to enable MRAM based cache memory for microprocessors. The L2 cache alone uses about 80% of the power consumed by the CPU, so reducing the power consumption of the cache is very important - and STT-MRAM may reduce this consumption by about 60%. It's not clear how close is this technology to actually being commercialized.
Toshiba's new STT-MRAM uses a dual-cell (2T-2MTJ) circuit in which the two MTJs have complementary resistive states (high and low resistive states). This eliminates the leak path and also increases the readout signal intensity - and so improves access speed. In Toshiba's cahce, the read time is 4.1 ns - very close to that of SRAM, while the write time (2.1ns) is similar to SRAM. Toshiba also implemented error correction mechanisms into the cache STT-MRAM chip.