Researchers suggest and demonstrate a new scheme of spin-orbit-torque (SOT) induced magnetization switching
Researchers at Tohoku University developed a new scheme of spin-orbit-torque (SOT) induced magnetization switching. In the new scheme the magnetization directed collinear with the current.
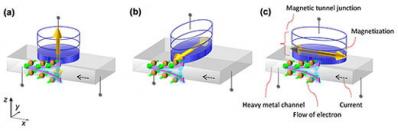
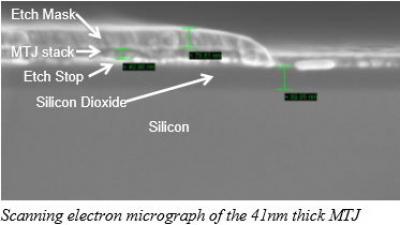
The researcher fabricated three-terminal devices with the new structure (using a Ta/CoFeB/MgO-based magnetic tunnel junction) and successfully demonstrated the switching operation. The research report a "reasonably small" required current density to induce the magnetization switching and a "reasonably large" resistance difference between 0 and 1 states. They say that this is a promising candidate for future MRAM devices.